- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
JAMA: Increased Risk of Vitiligo Observed in Transplant Recipients
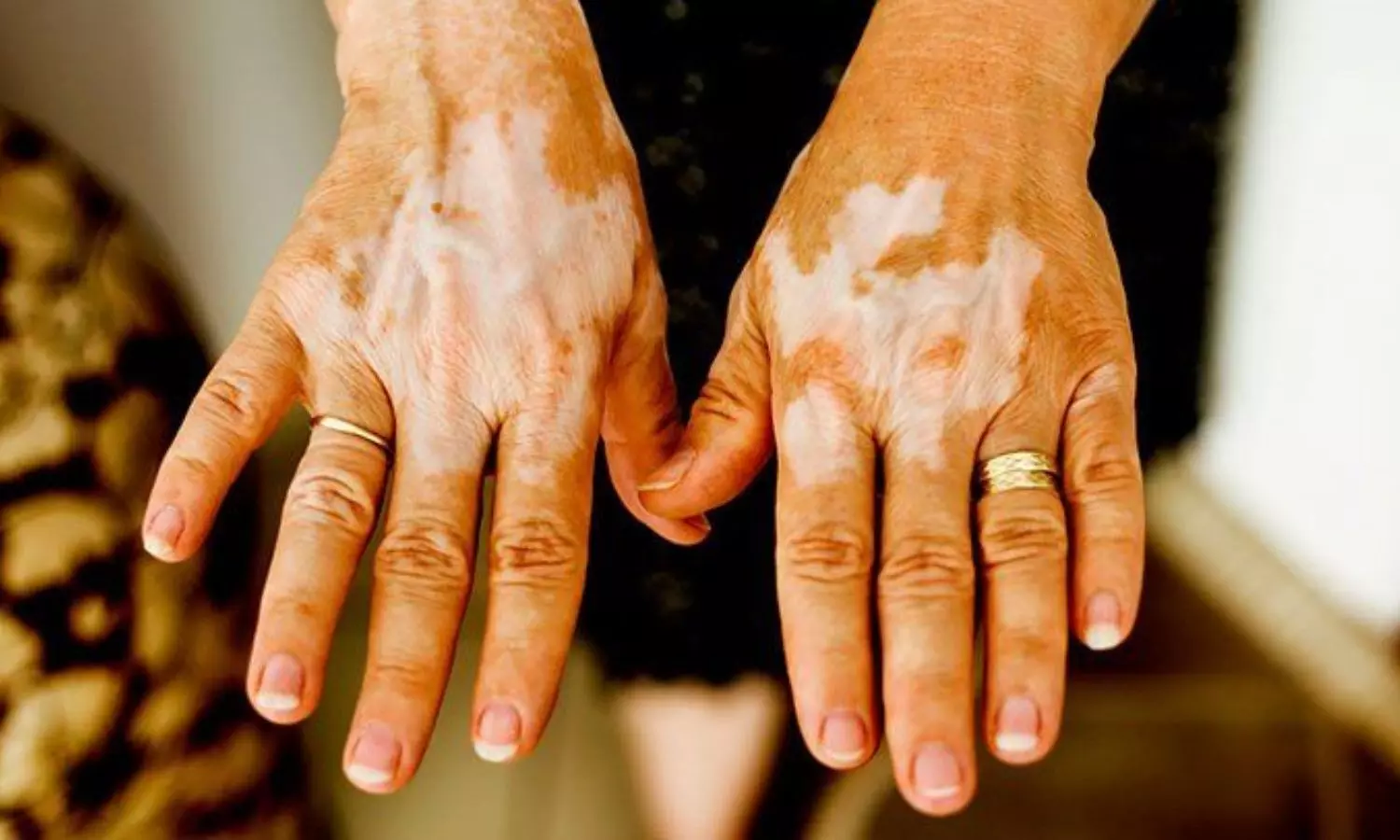

Vitiligo is characterized by the selective loss of melanocytes, but the large-scale studies assessing its occurrence in transplant recipients specially those with graft-vs-host disease (GVHD), have been rarely studied so far. In a recent cohort study by Chul Hwan Bang and colleagues, a significant correlation between solid organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplant (SOT and HSCT) recipients and an heightened risk of vitiligo was explored. The findings were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The study utilized data from the National Health Insurance Service database of Korea and included patients of 20 years or older. These participants underwent transplantation from January 2010 to December 2017, with follow-up until December 2019. A total of 119,145 individuals were grouped as age- and sex-matched controls who provided the benchmark for comparison.
The analysis was conducted from July to December 2021 revealed that the 23,829 transplant patients studied exhibited a higher risk of vitiligo compared to their non-transplant counterparts (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR] of 1.73; 95% CI, 1.35-2.22). Also, kidney and liver transplant recipients showed a slightly increased risk, but the most important findings were observed in HSCT recipients by indicating an AHR of 12.69 (95% CI, 5.11-31.50).
Further stratification revealed that those who had received allogeneic grafts, autologous grafts, patients with comorbid GVHD, and those without GVHD all demonstrated higher vitiligo risks compared to the control group.
The key findings of this research emphasize the imperative for clinicians to be cognizant of the increased risk of vitiligo in transplant recipients, specially in the context of HSCT, GVHD, and the type of graft received. This understanding urges a multidisciplinary approach in monitoring patients to bridge dermatology and transplantation medicine. With this outcome, clinicians can customize their strategies to offer more vigilant care to those at high risk, ultimately improving the management of transplant recipients.
Source:
Bang, C. H., Park, H. E., Kim, Y. H., Jung, J.-H., Lee, J. H., Park, Y. M., & Han, J. H. (2023). Risk of subsequent vitiligo in transplant recipients with comorbid graft-vs-host disease. JAMA Dermatology (Chicago, Ill.). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.4933
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in