- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Heavy Metal Exposure linked to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Risk
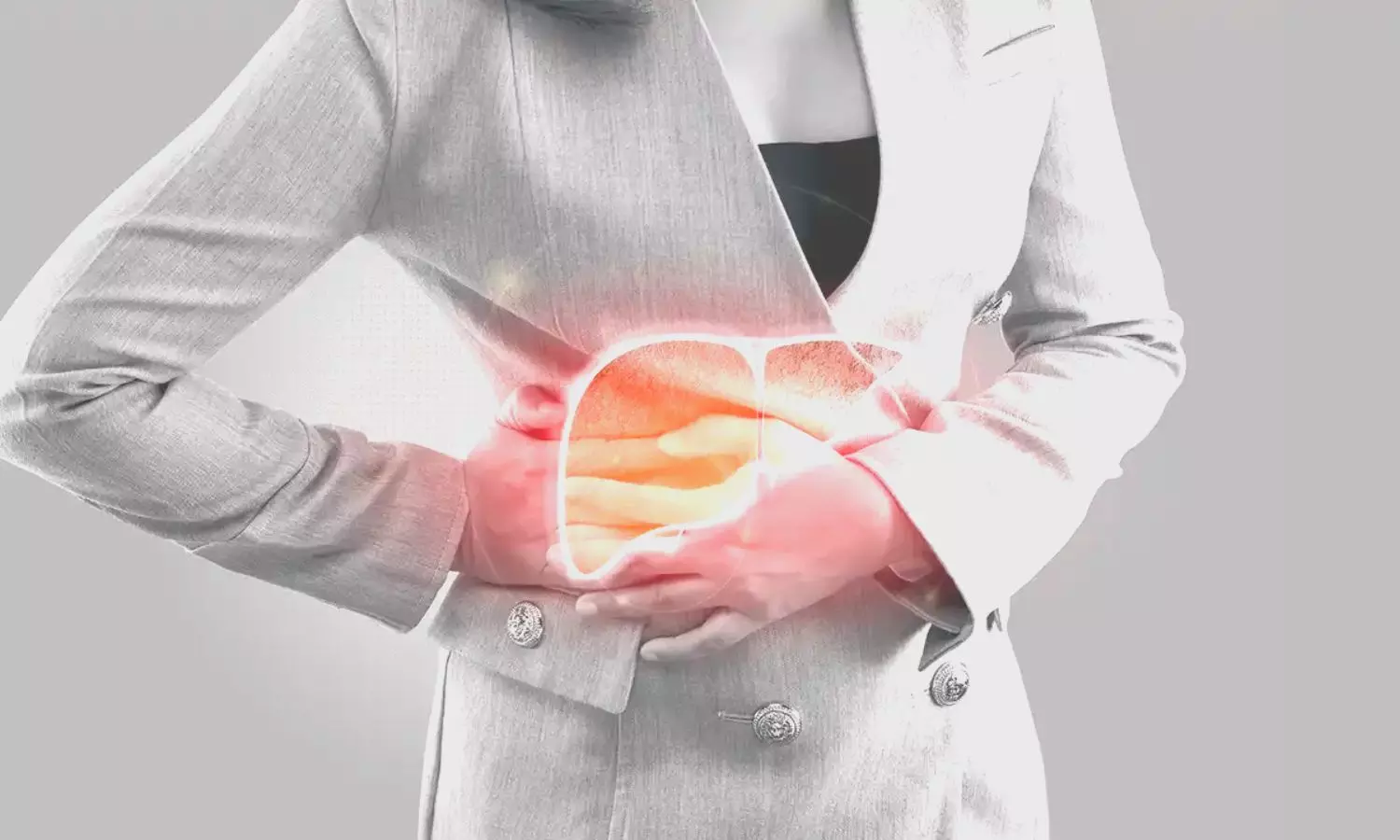

A recent study by Yuguang Li and team unveiled the critical association between heavy metal exposure and the occurrence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MASLD) among US adults. The findings were published in the Frontiers in Nutrition.
This cross-sectional study involved 6,520 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and spanned from 2011 to 2018. MASLD is a condition often associated with obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance, has been a subject of intensive research. But, the role of metal exposure in MASLD has remained largely unexplored. To address this gap the study undertook a comprehensive investigation to explore the potential links between blood levels of five heavy metals (mercury, manganese, lead, selenium, and cadmium) and the prevalence of MASLD.
The research found elevated blood selenium levels as a contributing factor to an increased likelihood of MASLD in US adults. Also, blood lead exposure demonstrated a positive correlation with MASLD risk. And, no significant association was observed between blood cadmium, mercury, manganese levels, and the risk of MASLD. Importantly, blood cadmium exposure emerged as the primary contributor to MASLD risk among the five metals studied. The outcomes revealed a nuanced interplay, emphasizing the critical role of specific heavy metals in the development of this liver condition.
In conclusion, this study looked into the previously underexplored facet of MASLD causation. The significant correlation was identified between blood cadmium and lead exposure levels and the occurrence of MASLD emphasize the need for further research and health interventions for public. This can reduce heavy metal exposure by potentially preventing or managing this increasingly prevalent metabolic disorder among US adults.
Reference:
Li, Y., Liu, Z., Chang, Y., Chen, N., Zhang, R., Liu, X., Song, W., & Lu, J. (2023). Associations of multiple toxic metal exposures with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: NHANES 2011–2018. In Frontiers in Nutrition (Vol. 10). Frontiers Media SA. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2023.1301319
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in