- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
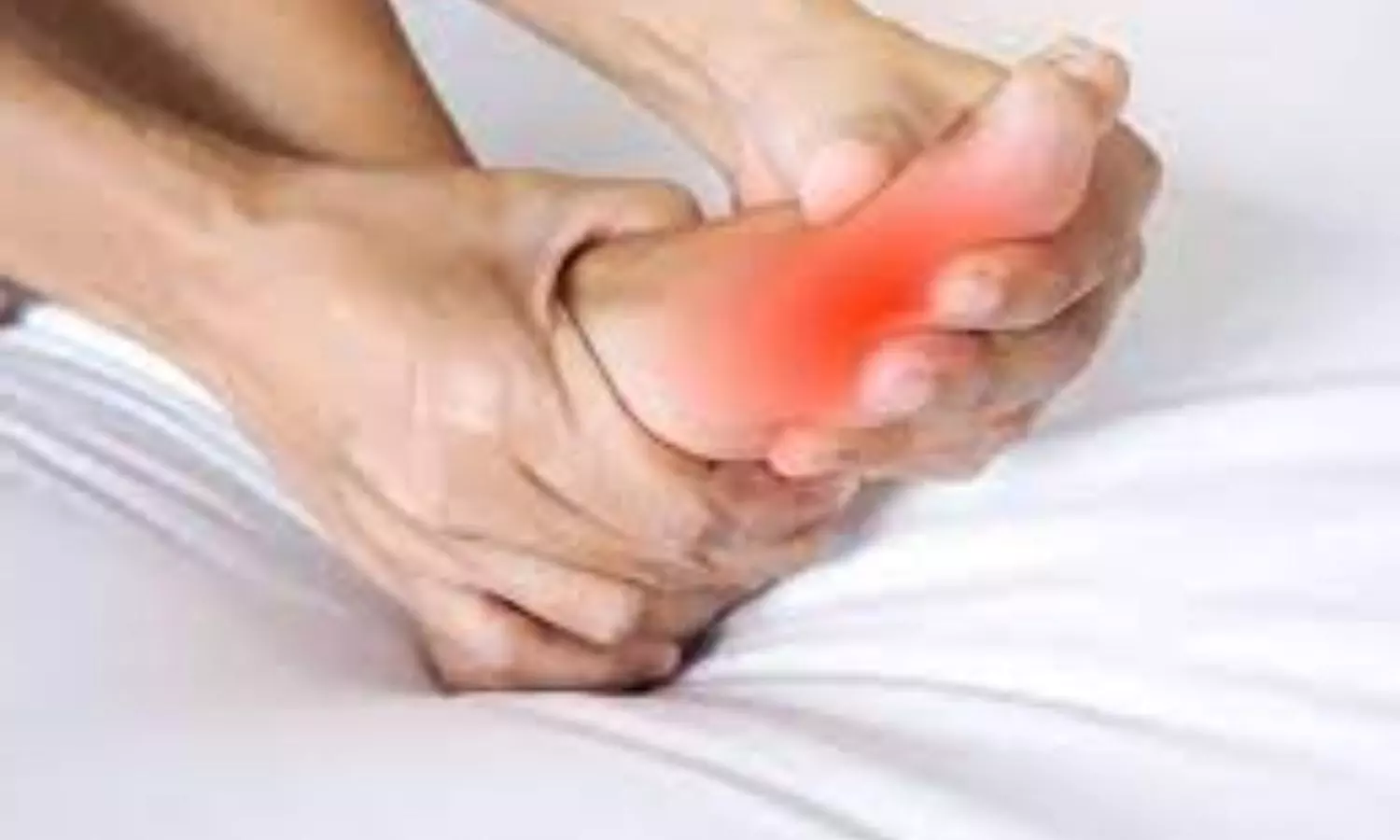
Breakthrough in Gout Treatment: Combined Regimen Promising in lowering Urate levels
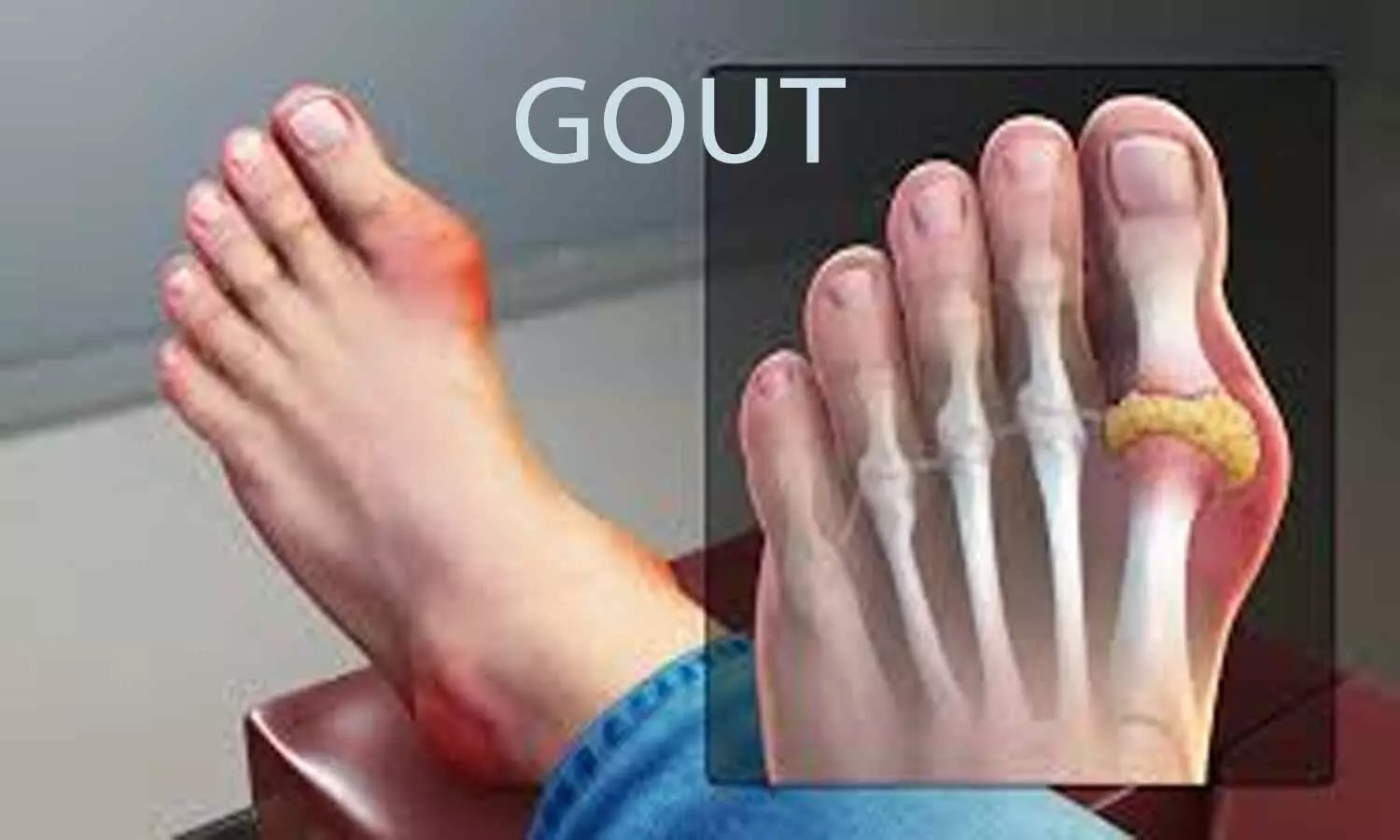
Gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis, often characterized by painful attacks, has long been managed through urate-lowering therapy (ULT). However, a recognized gap in care has led researchers to explore simpler ULT regimens that not only effectively target serum urate levels but also improve the overall quality of gout treatment. In a recent comparative effectiveness trial, a novel approach involving febuxostat monotherapy versus a combination of febuxostat and low-dose benzbromarone has shown promising results, especially in cases of gout with combined renal urate underexcretion and overload.
The study results were published in the journal Arthritis Care & Research.
The prospective, randomized trial enrolled participants with a specific type of hyperuricemia and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) above 60 ml/min/1.73 m2. Individuals were randomly assigned to either a combination therapy of febuxostat and benzbromarone or febuxostat monotherapy. The primary goal was to assess the proportion of participants achieving a serum urate (SU) level below 360μmol/L after 12 weeks. The study also investigated changes in liver and kidney function, incidence of new-onset urolithiasis, and occurrences of gout flares.
- Out of the 250 participants initially randomized, 219 completed the 12-week treatment.
- The findings revealed that the group receiving the combination of febuxostat and benzbromarone exhibited a significantly higher success rate in reaching the SU target compared to those on febuxostat monotherapy (75.5% vs. 47.7%).
- The odds of success were approximately 3.37 times higher in the combination group.
- Importantly, the safety profiles were found to be comparable between the two groups, suggesting a favorable risk-benefit profile for the combination therapy.
Thus, this breakthrough could address the unmet need for simpler gout treatment strategies, potentially transforming the landscape of care for individuals dealing with this painful condition. As further research unfolds, this novel approach holds promise for becoming a viable option, offering hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those navigating the challenges of gout.
Further reading: Superiority of low dose benzbromarone add-on to low dose febuxostat compared to febuxostat monotherapy in gout with combined-type hyperuricemia. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.25283
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.